Research Experience
Starting out as a research assistant, I steadily expanded my skills in data analysis, manuscript preparation, and team coordination until I began leading my own research projects.
CURRENT PROJECTS
Adversity, Resilience, and Symptom Stability
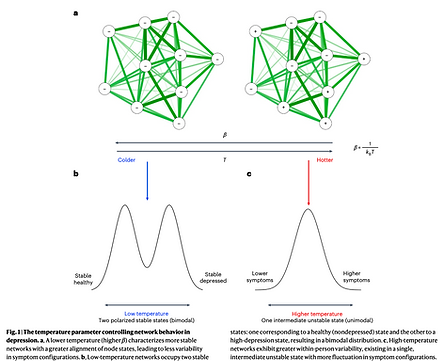
Illustration of the concept "network termperature".
Adapted from Grimes et al. (2025) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s44220-025-00415-5
Aims
This study aims to estimate a system-level stability metric ("network temperature") in adults and test whether childhood adversity raises temperature (instability), whether adult resilience buffers it, and how externalising behaviours (e.g., harmful drinking, cannabis use, risk-taking) relate. Identifying who has "hot" versus "cool" networks can sharpen timing and targets for prevention and treatment and add predictive value beyond symptom totals.
Analytical method
R. Ising; network temperature (T=1/β); Wald/bootstrapped tests; MHQ1→MHQ2 longitudinal.
Current status
In preparation.
Dataset
UK Biobank.
Contribution
Conceptualization; Methodology; Software; Formal Anaysi; Writing-original draft; Visualization.
PAST PROJECTS
Aims
This study aims to identify distinct constellations of parental bonding and childhood trauma in Chinese young adults and test how those profiles relate to adaptive vs. maladaptive coping in adulthood. Person-centred profiles were expected to differentiate coping beyond single-variable effects.
Analytical method
Mplus 8.11; R. Latent Profile Analysis; BCH equality-of-means tests; chi-square tests ; covariate-adjusted regressions and ANCOVA sensitivity.
Dataset
1,074 clinical outpatients, 18-25 years (M=22.07; 44% female), recruited at a tertiary psychiatric hospital in Shanghai. Primary diagnoses: Major Depressive Disorder 60.6%, Generalized Anxiety Disorder 11.1%, OCD 7.0%, Bipolar Disorder 6.7%.
Key findings
Three profiles are identified. Secure-Adjusted, Ambivalent-Strained, and Disorganised-Adversity showed graded differences: secure used more positive coping; disorganised relied more on negative coping.
Current status
Published, Journal of Affective Disorders.
Contribution
Co-first author. Conceptualization; Methodology; Software; Formal analysis; Data cruation; Writing-original draft; Writing-review & editing; Visualization; Project administration.
Aims
This study aims to examine how maternal/paternal behavioural control and adolescents’ voluntary disclosure relate to reactive vs. proactive aggression, and whether these links differ by gender in a large Hong Kong school sample. It addresses the gap that few studies have integrated parenting facets, aggression subtypes, and sex differences in East Asian contexts.
Analytical method
SPSS. Pearson correlations and full correlation matrices; assumption checks; independent-samples t-tests for gender differences; gender-stratified correlation analyses to compare mother/father control and disclosure patterns.
Dataset
Cross-sectional survey of 3,806 adolescents (1,925 boys; 1,881 girls), ages 11-18 (M=13.2, SD=1.18), secondary 1-3 in Hong Kong; 5,482 biological parents (3,198 mothers; 2,284 fathers) also completed questionnaires.
Key findings
Parental control was reliably linked to lower proactive aggression and delinquency (stronger in same-gender parent-child dyads), while adolescent disclosure to parents was the strongest, broad protective factor across aggression, delinquency, anxiety/depression, and attention problems.
Current status
Under review, Journal of Adolescence.
Contribution & Roles
First and corresponding author. Methodology; Software; Formal analysis; Data cruation; Writing-original draft; Writing-review & editing; Visualization.
Aims
This study aims to model the directed relationships among self-compassion, compassion for others, and prosocial behaviour in adolescents, and test whether network structure differs between the United States (individualistic) and Hong Kong (collectivistic). The goal is to generate testable pathway hypotheses that can inform future intervention and longitudinal work.
Analytical method
R (bootnet). EBICglasso; case-bootstrap accuracy/stability; centrality; Bayesian networks; consensus graphs (≥85% inclusion); 10-fold cross-validation; AIC/BIC.
Dataset
2,313 adolescents, ages 13-17 (M=15.53, SD=1.24); 51.5% female, 46.7% male, 1.8% non-binary/other. Recruitment: 63.2% United States (racially diverse), 36.8% Hong Kong (predominantly Asian).
Key findings
Kindness most directly predicted prosocial behavior in both samples
Cultural paths diverged:
-
Hong Kong: kindness → mindfulness → prosocial behaviour
-
U.S.: mindfulness → kindness → prosocial beahviour
Current status
Under review, Journal of Youth and Adolescence.
Contribution & Roles
Co-first author. Methodology; Software; Formal analysis; Data cruation; Writing-original draft; Writing-review & editing; Visualization.
Aims
This study aims to develop a brief and culturally grounded scale to assess shame and guilt in Chinese fathers raising children with developmental disabilities, and establish a robust factor structure and reliability for use in research and practice.
Analytical method
R. Explanatory factor analysis; confirmatory factor analysis; multi-index fit (CFI/TLI, RMSEA, SRMR); reliability (α, Ω, CR).
Dataset
437 biological fathers in Hong Kong; children aged 2–12 with DD (e.g., ASD, ADHD, ID).
Key findings
Clear two-factor solutions for each construct
-
Shame: perceived inter-level of failure & perceived intra-level of failure
-
Guilt: cognitive wrongdoing & emotional wrongdoing
Current status
Under review, Current Psychology.
Contribution & Roles
Third author. Methodology; Software; Formal analysis; Data cruation; Writing-original draft; Writing-review & editing; Visualization.
Aims
This study aims to translate, culturally adapt, and validate a short Father Involvement Scale for Hong Kong Chinese fathers of children with developmental disabilities; establish a defensible factor structure and reliability for service and research use.
Analytical method
R. Explanatory factor analysis; confirmatory factor analysis; multi-index fit (CFI/TLI, RMSEA, SRMR); reliability (α, Ω, CR).
Dataset
437 biological fathers in Hong Kong; children aged 2–12 with DD (e.g., ASD, ADHD, ID).
Key findings
A four-factor, 25-item solution with good fit and strong reliability.
Factors:
-
Educational & Rehabilitation Support
-
Independence Training
-
Emotional & Social Engagement
-
Physical Care
Current status
Under review, Child Psychiatry & Human Development.
Contribution & Roles
Second and corresponding author. Methodology; Software; Formal analysis; Data cruation; Writing-original draft; Writing-review & editing; Visualization.
Aims
This study aims to test how three daydreaming styles, including positive-constructive (PCD), guilt/fear-of-failure (GFD), and poor attentional control (PAC), relate to objective and subjective underachievement in high-ability teens, and whether self-compassion mediates (or suppresses) these links.
Analytical method
Stata 18; R. Covariate-adjusted logistic regressions; Karlson–Holm–Breen (KHB).
Dataset
983 high-ability adolescents, 13–17 years (M=15.6, SD=1.2), 47.6% female; 67.4% U.S., 32.6% Hong Kong; ethnically diverse.
Key findings
PCD and self-compassion lowered underachievement risk; GFD and PAC raised it; self-compassion fully mediated and reversed GFD’s link with subjective underachievement (suppression).
Current status
Under review, Child Psychiatry & Human Development.
Contribution & Roles
Third author. Conceptulization; Methodology; Software; Formal analysis; Data cruation; Writing-original draft; Writing-review & editing; Visualization.
Aims
This study aims to test whether the classic in-group advantage in emotion recognition extends to retrodicting which event caused a reaction, and examine how cultural familiarity shapes accuracy.
Analytical method
R. Wilcoxon rank-sum/signed-rank with Benjamini–Hochberg FDR; effect sizes as rank–biserial r; Aligned Rank Transform for nonparametric factorial tests.
Dataset
Stimuli: 56 filmed reactors (24 Asian/Chinese, 32 European).
Main experiment: N=114 adults (65 Chinese, 49 European, 22-28 years). Stimuli set: 20 Chinese, 36 European clips
Key findings
Participants reliably retrodicted events; Waiting highest and Joke lowest accuracy. European participants were more accurate overall and showed a clear in-group advantage (especially for compliments). Chinese participants showed no in-group advantage and occasional out-group advantages (better with European stimuli for joke/story), yielding an asymmetrical pattern likely shaped by accommodation and cultural display rules.
Current status
Published, Asian Journal of Social Psychology.
Contribution & Roles
First and corresponding author. Conceptulization; Methodology; Software; Formal analysis; Data cruation; Writing-original draft; Writing-review & editing; Visualization.
Take this fun experiment here (English Version; Chinese Version)!
Aims
This study aims to test whether Cultural Intelligence (CQ) mediates the link between Openness to Experience (OE) and Acculturative Stress (AS) in Mainland Chinese students studying in Hong Kong, and explore subgroup differences by social integration (local friendships).
Analytical method
SPSS PROCESS. Data-quality screening and timing-based exclusions; Bootstrapped stepwise regressions; Mediation analysis; back-translation for bilingual materials.
Dataset
111 Mainland students enrolled at HK universities; cross-sectional online survey with validated AS, OE, and CQ scales.
Key findings
OE predicted lower AS; CQ did not mediate overall, but fully mediated the OE→AS link among students with fewer local friends (conditional indirect effect).
Contribution & Roles
Conceptulization; Methodology; Software; Formal analysis; Data cruation; Writing-original draft; Writing-review & editing; Visualization.








